Table of Contents
Introduction to Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
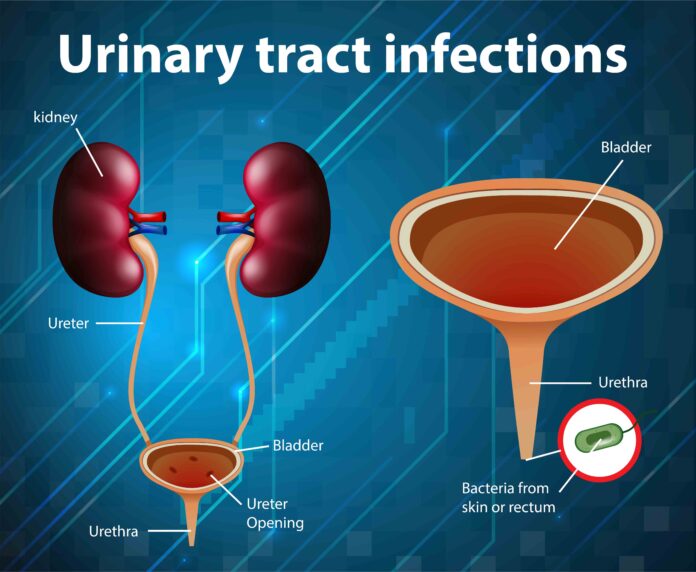
As a healthcare professional, I frequently encounter patients with urinary tract infections (UTIs), one of the most common bacterial infections. A UTI can affect any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The infection often involves the lower urinary tract—the bladder and the urethra. UTIs are particularly common in women, but men, children, and older adults can also be affected.
What is an Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
In my practice, I often explain to patients that a urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and begin to multiply. The most common cause of UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria that typically lives in the digestive system. However, other bacteria, viruses, and fungi can also cause UTIs, though these cases are less frequent.
Common Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections
Identifying the signs and symptoms of a UTI early is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Based on my experience, the most common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urge to Urinate: Patients often report an increased need to urinate, even if little comes out.
- Burning Sensation During Urination: A burning feeling while urinating is a hallmark sign of a UTI.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Noticeable changes in urine, such as cloudiness or a strong odor, are common.
- Pelvic Pain: Especially in women, pain in the pelvic area can be a significant symptom.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, may appear pink, red, or cola-colored.
- Fever or Chills: A fever might indicate that the infection has reached the kidneys, necessitating immediate care.
What Indicates an Urinary Tract Infection?
As a healthcare provider, I advise patients to look for several indicators that might suggest a UTI:
- Persistent Urge to Urinate: A frequent and intense urge to urinate is often the first sign.
- Discomfort or Pain: Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvic region can signal a UTI.
- Changes in Urine: Any noticeable changes in the appearance or smell of urine should not be ignored.
- General Malaise: Feeling unusually tired or unwell, especially when combined with other symptoms, may indicate a UTI.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
From a medical standpoint, the primary cause of UTIs is the migration of bacteria from the digestive tract to the urethra. Women are particularly at risk due to their anatomy, as their shorter urethra allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. Other risk factors include:
- Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Specific Types of Birth Control: Diaphragms and spermicidal agents may increase UTI risk.
- Menopause: Post-menopausal women experience changes in estrogen levels that affect the urinary tract.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Some individuals are born with abnormalities predisposing them to infections.
- Suppressed Immune System: Those with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to UTIs.
Diagnosis and Treatment
When diagnosing a UTI, I typically recommend a urine analysis to check for the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells. A urine culture may also be performed to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment usually involves antibiotics tailored to the specific bacteria in the urine culture. Staying well-hydrated and urinating frequently can help flush the bacteria from the urinary tract, complementing antibiotic treatment.
Prevention of Urinary Tract Infections
Preventing UTIs is possible through simple but effective measures. I often suggest the following to my patients:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Hydration is vital to diluting urine and flushing out bacteria.
- Wipe from Front to Back: This practice helps prevent bacteria from spreading to the urethra.
- Empty Your Bladder After Intercourse: Urinating after sex can help remove bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
- Avoid Irritating Feminine Products: Deodorant sprays and douches can irritate the urethra, increasing infection risk.
- Wear Cotton Underwear: Cotton promotes better air circulation, which can reduce bacterial growth.
You May Like The Following:
Standard Process ProSynbiotic: Unraveling its Powerful Ingredients, Benefits, and Expert Review
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are common but manageable with the proper knowledge and care. As a medical professional, I emphasize the importance of recognizing the early symptoms of a UTI and seeking prompt treatment to avoid complications. Preventive measures, such as good hygiene and staying hydrated, are crucial in reducing the risk of UTIs.
If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to a quicker recovery and prevent more severe health issues.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Untreated Urinary Tract Infections?
Untreated urinary tract infections (UTIs) can lead to severe complications, including kidney infections and chronic kidney damage. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking medical treatment to avoid these long-term effects is essential. Ignoring a UTI can also increase the risk of sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection.
Can Men Get Urinary Tract Infections?
Yes, men can get urinary tract infections, though they are less common than in women. An enlarged prostate, kidney stones, or urinary tract abnormalities can cause UTIs in men. Symptoms in men often include pain during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and sometimes blood in the urine. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications.
What Foods Should Be Avoided During an Urinary Tract Infection?
Certain foods can irritate the bladder and worsen UTI symptoms. It’s advisable to avoid spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic fruits like oranges and tomatoes during a UTI. Instead, focus on a balanced diet with plenty of water to help flush out the infection.