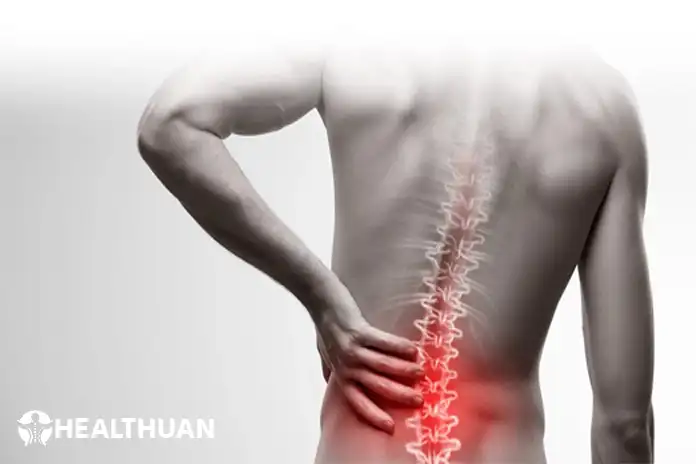
Back pain is a common problem for almost all people around the world. It’s hard to find people who haven’t experienced back pain at least once in their lives. Backache occurs from muscles, ligaments, nerves, bones, joints, cartilage, or discs. Anyone of any age can suffer from backache at some time in life.
Around 90 percent of people suffer from low back pain at some point in their life span. Low backache stands the fifth position among all medical conditions. The Good news is that Ninety percent of backaches don’t need any surgical treatment.
In this article, we will shed light in depth to know about back pain.
Causes of Back ache
Why is back pain? Remember, back pain is not a disease, just a symptom of the disease. However, a research study shows that in 90 percent of cases, no specific cause of back pain was found. The patient usually feels this pain suddenly while lifting a heavy object. Back pain is felt when the muscles and ligaments on the side of the spine are injured, i.e., if there is tension or sprain. In this case, the pain may get better in a few weeks. Exercise and pain medication is enough to get well.
Mechanical causes
1) If the chair and table are not sitting properly or if you are not sitting properly or leaning back and forth, severe pain may occur in the waist.
2) Sitting for a long time and working in the same manner, the pain in the waist is severe.
3) For Those who read books or do other activities while lying down or leaning, their spine is damaged, and pain is felt.
4) Many people do not lift heavy things properly. Pulling weighty things puts pressure on backbones and causes pain.
5) Backache might occur while we do our daily functional activities in daily life, such as
6) Coughing with forwarding bending position in standing or sitting
Awkward forward bending due to tie a shoelace or picking up any object from the floor.
7) Long timing driving or journey without a break
8) Sleeping on a mattress that is soggy and curvy like foam or old spring.
Structural causes
1) In our back spine, One bone is attached to another bone; the space between them is the intervertebral disc. Suppose the disc becomes ruptured due to uneven stress or imbalance in chemical structure. In that case, the disc puts pressure on the spinal nerve that causes backache.
2) Back pain in women after the age of 30-35 due to bone loss problems.
3) Sciatic nerve compression or the back part of thigh muscle spasm causes back pain. Sciatic pain occurs from disc herniation or ruptured disc, often called backache.
4) Vitamin D deficiency leads to low bone density, which causes the backbone and muscle ache to become weak. As a result, backache starts from impaired function of bone and muscle of the back spine. Osteoporosis and osteopenia, spondylosis, spondylolisthesis cause backache.
5) Abnormal spinal curves from birth like kyphosis or scoliosis causes backaches. Excessive lateral curvature (Scoliosis) or forward curvature (Kyphosis) of backbone compresses disc. A long time in a bad position of working could also result in kyphosis or scoliosis.
Medical conditions
- Spinal cord lesions such as Cauda Equina syndrome are a medical condition where the lower end of the nerve root bundle of the spinal cord has severe inflammation, resulting in backache with paralysis. Pain occurs at the buttock, thigh, and groin area.
- Bone tumor/cancer or bone tuberculosis causes backbone ache. Besides, General weakness of the body may easily lead to back muscle sprain due to sudden pull or cramp.
- Infection of the spine such as pelvic inflammation, urine infection or shingles, transverse myelitis causes unbearable backache, which might be life-threatening also.
Types of backache
Back pain may be acute or chronic. Acute backache persists for 72 hours to a month. On the other hand, chronic backache lasts for three months to a year(s). Moreover, it is important to identify the types of backache for better diagnosis and treatment planning. Besides, the followings are some types of backache :
- Mechanical or axial pain
Mechanical backache is also referred to as Axial pain. The nature of this kind of pain exists within a confined area such as the lower back area or hip/thigh. Mechanical pain aggravates while working or traveling for a long time. Activity is the triggering factor for axial pain. Axial ache gives you dull ache or throbbing types of sensation. This pain comes in and out but remains in a constant area. Sudden muscle twisting or strain or a mild level of disc herniation causes mechanical pain.
- Referred pain
When pain travels from back to thigh or hip, then it is called referred pain. The referred pain is dull or sharp shooting pain moving from one area of the body to other parts. Disc ruptured, or degenerative changes of the backbone might cause this type of backache. Pain on the waist to the backside of the thigh is the common site of referred pain.
- Radicular pain
Radicular pain is described as it travels from the waist to the leg. This radicular pain sensation might sharp shooting nature or a burning sensation down the leg. Spinal nerve compression or inflammation of spinal nerve roots produces radicular pain. Partial or total numbness of leg signs also indicates this kind of pain.
- Upper / Thoracic back pain or Middle backache
Thoracic region means the region starts from below the neck area up to the waist area or the upper level of your belly button. Twelve spinal backbones comprise the thoracic area of the body. So pain in this area might refer to moderate back pain.
- Lower back pain
The lumbar area comprises 5 spinal vertebrae with its surrounding soft and hard structures. Pain in this area is very common among wedge workers, desk jobholders, students, and women.
Read more:

Pain: A latest guide for you 2023
Symptoms (Commonly seen) of backache
Dull type pain or sharp burning ache on the lower back
- Pain traveling around the back
- Ache that shooting down to either one or both leg
- Pain aggravates while at rest or activity
- Prolonged walking causes severe cramp on thigh and back muscle
- Numbness of one leg or both.
Risk factors of backache:
1. Low back pain usually increases with age. It is more common after the age of 30 to 40 years.
2. Lack of physical labor or regular exercise can lead to abdominal and back muscle strain. As a result, a little hard work can cause pain.
3. Excess weight puts pressure on the lumbar muscles and bones. The result can be a pain.
4. Arthritis causes deterioration and damage of the cartilage resulting in backache.
5. Nutritional imbalance within the intervertebral disc causes insufficient shock-absorbing properties. Spinal nerves get hurt, leading to back pain.
6. Many times, kidney stones or urinary tract infections can cause back pain. However, in that case, there will be not only back pain but also many other symptoms. So if you have back pain, it is not a kidney stone or urinary infection.
7. Depression or stress is the potential cause of back pain. Research studies show mental depression or anxiety causes inflammation and pain of joints and muscles. When stress hormones are released excessively, it releases some chemicals like cytokines which suppress your immune system. So your body gets injured easily.
8. Pregnancy can impact your spinal structure and cause lower backaches. During pregnancy, different relaxation hormones relax mothers’ joints and bodies. So, after pregnancy, these excessive relaxed muscles and joints cause backaches.
9. Local anesthesia on the spine during surgery is the major cause of back pain in Asian girls nowadays.
10. Sedentary lifestyle with alcohol and smoking causes back pain. Smoking causes the blood vessels to become thinner, and blood does not flow properly from the waist down.
When back pain is not a cause for fear: –
- It is considered normal to have back pain if you sit and work for a long time or get up after traveling long distances.
- People who are overweight have back pain. In this case, weight loss will reduce back pain. However, if you do not lose weight, this pain will be permanent.
- There may be back pain during pregnancy. About 50 to 60 percent of women suffer from low back pain during pregnancy. The pain goes away after delivery. However, many times there is back pain after a cesarean operation. If so, you need to take the advice of a doctor.
- Urinary tract infection can cause back pain. In this case, the back pain gets better if the treatment is confirmed by combining it with other symptoms.
- Low back pain during menstruation or period.
- Viral fever can cause back pain even after fever.
- If you wear high-heeled sandals for a long time or if you wear such sandals for a long time.
Warning signs of back pain
- Any changes in urination or bowel movements along with back pain.
- Backache accompanied with fever.
- The intensity of the pain is severe and does not decrease even if you take a rest.
- Leg or cuff muscle atrophied or total numbness of the foot.
- Ache goes down one or both legs, especially below the knee.
- Pain associated with weakness, numbness, or numbness in the legs.
- Weight loss occurs with pain.
If such symptoms occur, consult with your Neurosurgeon immediately.
Diagram of back muscle to understand back pain
Our back muscles start from the backside of the skull, further extending to the shoulder, down to back above hip level. These muscles attach with ribs, vertebral bone(spine bone), shoulder blade, and neck area.
Courtesy: gretty image.
Back muscles help move our head, neck, shoulder, arms, and legs in a coordinating way. Our muscles work as a group to bending, twisting, straightening, and rotating our bodies. Back muscles can divide into two sections according to their arrangement—superficial and Deep muscles layer.
Superficial muscles: These muscles move our arms, elevate the shoulder, and rotate the spine. It also keeps our spine erect. These muscles are as follows:
Latissimus dorsi: it supports us to rotate our shoulder, arm, and moving arm on the backside.
Levator scapulae: it elevates our shoulders, such as shrugging of shoulders.
Rhomboids major and minor muscle: It helps to move our shoulder inward toward the spine.
Trapezius: this muscle helps to raise our arms, scapula and stabilize our back spine as well.
Deep muscles: There are three deep back muscles as Semispinalis, Multifidus, and Rotators.
Semispinalis muscles extend our head, neck, and upper back. It supports side bending of the upper back.
Multifidus muscles stabilize our spine in an erect position. It supports side bending and rotation of the spine.
Rotator muscles rotate the spinal vertebrae on the same side and opposite side.
Diagnosis of back pain
Diagnosis of back pain early is very important to minimize permanent damage of the spinal disc or nerve. To ascertain back pain and its extent of damage is very crucial for the betterment of backache.
Physical test:
Physicians or Physical Therapists will do some movement tests of the back, like bending forward or backward. A doctor will ask which factors aggravate back pain. Do you have any medical history like trauma, diabetes, Asthma, Gastritis, Hypertension, Hypothyroidism, etc.?
Blood test:
Total blood count, hemoglobin count, Ferritin test, calcium level, vitamin D, creatinine, CPK, serum uric acid are usually advised to sort out the association of back pain.
X-Ray :
X-Ray is the classical and primary test for backache diagnosis. This test shows the bone alignment, any degenerative changes, or any anomalies.
MRI :
Magnetic Resonance Image shows the delicate soft tissue structure of our body. Any back pain problems on ligaments, muscles, discs, tendons injury can be precisely viewed through MRI.
CT Scan:
A Computed Tomography scan shows hard structures like the skull or any bony portions more specifically and in detail compared to X-ray. But it is not as detailed as the MRI shows in low back pain.
EMG:
Electromyography shows muscle activity level plus the extent of its damage or injury on particular muscles or groups of muscles. Back spinal muscles problems can easily be identified through this test.
NCS:
Nerve Conduction Study shows which nerve has damaged and what extent that can readily identify through nerve conduction study. When a spinal nerve gets compressed and it damages its corresponding nerve,NCS provides a very specific diagnosis of a particular nerve injury.
Treatment of back pain
Management of back pain can classify into the following:
Drug-free treatment
Heat application
In chronic back pain, heat can apply to painful sites. But for the first 72 hours of acute injury, heat is not recommended to apply on the injured site.
Physiotherapy, Exercise, and Traction
Back pain treatment must be provided through a licensed Physical Therapist. Proper assessment and effective therapeutic management can apply by the qualified Physiotherapist.
Alternative therapy: These include:
- Yoga(exercise) is the stretching exercise of different parts of the body. Yoga can relax stiff back muscles.
- Acupuncture treatment is the ancient Chinese medicine for back pain. Acupuncture means needles at specific points in the body to relieve pain.
- Chiropractic treatment is the current treatment method for back pain injury. It requires academic knowledge to mobilize the back spine. Chiropractor professionals apply control thrust and force over backbones to relieve stiffness.
- Spiritual methods such as meditation, biofeedback, and behavioral change, also help relieve pain.
Medical treatment
Medication for managing chronic back pain becomes essential to relieve acute back pain. Among the prescribed drugs:
Paracetamol /Acetaminophen: This medicine is usually the first medicine prescribed for back pain. It also has fewer side effects.
Nonsteroidal drugs: Nonsteroidal drugs healing drugs include ibuprofen and naproxen. When paracetamol cannot relieve pain, then this analgesic drug applies to reduce pain—painkillers on the market as creams, ointments, and sprays. Spray can apply any part of the body that helps reduce the severity of the pain.
Muscle relaxants: Back pain causes muscles of the back to get stiffed or spastic—muscle relaxant medicines, applied by doctors to relax the tight muscles.
Opioids like Drugs: Pathedine and morphine are steroidal analgesics that effectively relieve acute pain. Adverse drug reactions such as drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth, and long-term use are prohibited.
Antidepressant drugs: The drugs used for chronic back pain who are suffering from long-lasting pain. These include amitriptyline, duloxetine, and imipramine.
Steroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisolone, help relieve lower extremity pain. They also reduce the inflammation (swelling) and swelling at the injury site that causes back pain.
Convulsive: Recent studies show anti-epileptic drugs with painkillers are effective in chronic back pain. Carbamazupine, gabapentin, and valproic acid are the most used anti-epileptic drugs. Confusion, gastric (stomach) upset, and headache are side effects caused by anticonvulsant drugs.
Surgery
When non-surgical treatment cannot reduce pain, doctors recommend surgery. Radiating pain, severe muscle weakness, spinal fractures need an operation.
Operation is required in emergencies like trauma and Cauda Equina syndrome. These conditions can lead to paralysis (numbness in the body) along with back pain.
Spinal fusion is a process where the vertebral disc is cut and connected. This procedure ensures there is no movement between them. It helps to relieve pain (arthritis) in the spine.
Laminectomy operation is done by removing the lamina that puts pressure on the nerve. This procedure follows while spinal stenosis occurs. Stenosis occurs when the spinal canal is narrowing, which causes back pain.
Foraminotomy operation is done to widen the spinal canal. This operation widens the space between the spinal cord and the passage of nerves.
In a Disc-tectomy, all or part of the disc has come out of its original position. It relieves the pressure exerted on the nerves by the protruding disc.
Although each process has risks, surgery relieves pain, freedom of movement, increased work productivity.
How to prevent back pain with home remedies
Home remedies for back pain mean managing the pain and normalizing the movement of the waist. Even if the acute pain subsides, weight lifting, twisting positions, extra physical exertion, and leaning forward should be stopped.
You need to practice sitting properly and use back support if necessary. Take a hot bath (hot pad, hot water bottle, or warm water bath). Exercise to make the muscles flexible and strong. You can also follow some more rules, such as.
Cold and heat therapy at the same time is very much effective for back pain. Firstly cold, then heat around 10 minutes can relieve your ache effectively. After a while, cold press water or ice again. If you do this for a few days, you will get relief, even if the pain does not go away completely.
Fix the place of work. Doing a desk job, make sure that the chair’s back is at a 90-degree angle and that the legs are kept evenly on the floor.
Eat food for bone nutrition. Fish oil, coral fish, yogurt, oat, cow milk, and vegetables contain a rich source of vitamin D.
- Quit smoking: Smoking creates arterial walls thick, so blood flow reduces to the spine. It also activates the cough, which can further worsen the back pain.
- Improve your posture: Keep your body weight in balance with the weight format above the legs. Proper posture is to maintain a normal curve in the spine while sitting and standing. An incorrect or defective posture puts pressure on the back muscles and leads to chronic back pain.
It is also important to maintain a proper posture to avoid straining the back muscles when lifting and carrying heavyweights.
Conclusion
Back pain is not always fully recoverable. It is managed by modifying your lifestyle, diet, and exercise. Proper diagnosis and healthy living are the main keys to keep away from back pain.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) of Back pain
-
What is the best treatment for backache?
Although it is not simple to answer in a word, stretching, strengthening exercise is the best approach to treating back pain. Ho, cold therapy, along with healthy living, is the best treatment for backache.
-
How to get relief from Back pain during pregnancy?
Back pain occurs during the six months of pregnancy; as the belly gets bigger, more weight puts pressure on the mother’s backbone. General free hand exercises, good posture maintenance, and a healthy diet will prevent back pain. Heat can apply to the backside of the pain aggravates. Exercise must be taken with the active guidance of a Physical Therapist who is an expert in this field.
-
How is Back Pain Associated with UTI?
Urinary tract infection causes lower abdomen pain which might travel to the backside of the hip also. Taking antibiotics for UTI could cure backache associated with a bladder infection.
-
Can you permanently fix back pain?
Permanently fixing back pain depends on how severe the pain is and the damage to the spinal nerve and disc. Continuously strengthening, stretching, and protecting the back muscles, back pain can ideally stop or recover. Besides, severe cases of back pain can’t always be cured by medical treatment.
-
Is Surgery the Ultimate Solution to Back pain?
The answer is No. After surgery, you have to make some lifestyle modifications, follow some restrictions of vigorous movement through a lifetime. It is recommended to try out non-surgical treatments like drugs, physical therapy, and alternative therapy for six months. When conservative management fails, then surgery can be performed to recover backache.